Last updated on March 2nd, 2025 at 03:23 pm
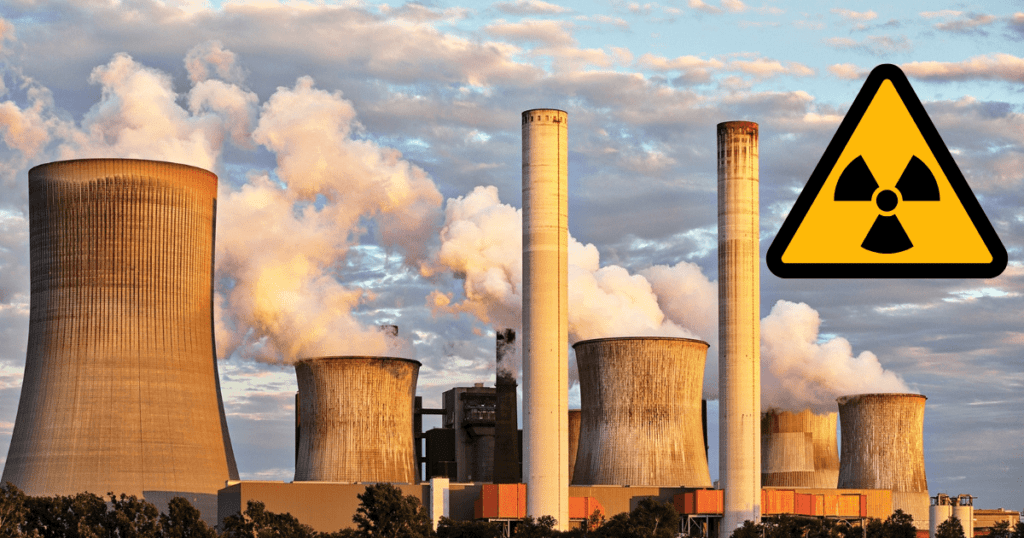
Non-renewable energy sources, for example, crude oil, coal and natural gas are derived from finite sources and can’t be replenished. In recent times or at least in the last few years, probably you have heard a lot about non-renewable energy sources, fossil fuels, and their impact on the environment such as greenhouse emissions, global warming, and climate change. Our modern society is still heavily dependent on non-renewable energy sources for transportation, technology, and industrial growth.
After going through this article, you will unlock the full picture of non-renewable energy sources and their impact on our daily lives. Non-renewable energy has a tremendous influence on our environment, economy, health, and geopolitics.
What is non-renewable energy?
Non-renewable energy is energy that is derived from finite sources and can’t be replenished (the term replenish means: fill up again) or regenerated over a short period of time. Fossil fuels, for example, crude oil, coal and natural gas are the common sources of non-renewable energy.
Scientific communities predict that, these fuels formed during the Carboniferous period , around 300 million years ago; from the remains of dead plants and animals that have been buried and subjected under heat and pressure. The energy stored in these fuels is released when they are burned to produce electricity or fuel for transportation.
Why does non-renewable energy sources still dominate?
Despite the increasing availability of renewable energy sources, such as solar panel, wind turbines; non-renewable energy sources still now dominates for several reasons:
- Accessibility: Non-renewable energy sources are often more accessible and easier to extract than renewable sources. Fossil fuels can be extracted with relatively simple technologies. And we have built these technologies over many many years.
- Cost: Non-renewable energy sources, such as petrol or natural gas are cost-effective due to the established infrastructure for extracting and processing them. But to date, renewable energy sources are more expensive than non-renewables.
- Reliability: Non-renewable energy sources are often more reliable than renewable sources, as they can be easily stored and transported anywhere in the world. In contrast, renewable energy sources are often dependent on the climate of the location.
Understanding non-renewable Resources: What defines a non-renewable energy resource?
The origin of the non-renewable resources are natural. Following the US Department of Energy, these resources were formed millions of years ago from the remains of dead plants and wildlife. In short, when plants and animals die, their remains may sink to the bottom of oceans, rivers, or lakes, or they may be covered by sediment on land. Over millions of years, additional layers of sediment may accumulate on top of the remains, gradually burying them deeper and deeper.
On many occasions, the dead subjects are buried quickly, such as due to a volcanic eruption, landslide or other natural calamities. Once the remains are buried, they are protected from decomposition by the lack of oxygen and the pressure of the overlying layers of sediment, which can ultimately lead to the formation of fossil fuels. Since these types of processes can take millions of years, as a result, fossil fuels are considered non-renewable.
What are examples of non-renewable Resources?
The most common non-renewable energy sources are:
- Coal
- Oil
- Natural gas
- Nuclear energy
There are some other examples of non-conventional sources of non-renewable energy:
- Metals: Metals are an important part of the industry and technology and they are formed through different geological processes. Some metals, such as gold, iron, aluminum and silver are also considered non-renewable resources because they are finite and can only be obtained from mining.
- Minerals: Minerals are important for human beings as they are used for industry, nutrition and agriculture and they are slowly formed through geological processes. Many minerals, such as phosphorus and potassium and rare earth elements are considered non-renewable.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of non-renewable energy?
Advantages
- Reliability: Non-renewable energy sources are generally reliable and they are easily available around us.
- Cost-effective: Non-renewable energy sources are cheaper in the short term. But in long term, it is going to be more expensive.
- Efficient: Non-renewable energy sources have higher power density. It means that it has compact energy, which indicates that the burning of less amount of fossil fuels can provide a higher amount of energy.
Disadvantages
- Environmental Impact: Burning of non-renewable energy sources produces greenhouse gasses and it leads to global warming and climate change.
- Finite Resources: Non-renewable energy sources are finite resources and will eventually run out.
- Geopolitical Issues: Since most of the countries in the world don’t have fossil fuels, they are heavily dependent on fossil fuel-producing countries. In case of war or other political turmoil, the energy security and economy of non-fossil fuel-producing countries can be heavily affected.
What are the limitations of non-renewable energy sources?
Non-renewable energy sources are limited by their finite resources. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, were formed millions of years ago and are being consumed at a much faster rate than they can be replenished. This means that eventually, these resources will run out, and we will need to find alternative sources of energy.
According to research-based data from 2015, there are only 51 years of oil, 114 years of coal and 53 years of natural gas reserve left. Many other sources predict that the oil reserves of the world will be finished by 2052.
In addition to the issue of finite resources, non-renewable energy sources are also limited by geopolitical issues. Many of the world’s largest oil and gas reserves are located in politically unstable regions, which can lead to conflict and uncertainty in the energy markets. This can have significant economic impacts, as well as contribute to global political tensions.
How can we protect non-renewable energy resources?
Have you ever heard that, whatever is finite, will be finished one day? Since non-renewable energy resources are finite, there are measures that can be taken to protect them. Here are a few examples:
- Energy efficiency: By using energy-efficient appliances and practices, we can reduce our overall energy consumption and extend the life of non-renewable energy sources.
- Alternative energy sources: While non-renewable energy sources are still necessary for the time being, transitioning to alternative energy sources, such as wind and solar, can reduce our reliance on non-renewable energy and help protect these resources.
- Conservation: Protecting and conserving non-renewable energy resources can help extend their lifespan. This includes measures such as reducing energy waste, investing in renewable energy research and development, and enforcing regulations to minimize environmental damage caused by energy extraction and use.
What are the impacts of non-renewable energy sources in our daily lives?
There are several impacts of non-renewable energy sources on the environment, economy, health and industries. Let’s discuss them in detail.
How does the extraction of non-renewable energy impact the environment?
- Fossil fuel extraction: The extraction of fossil fuels can cause environmental damage, including deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil and water contamination. According to WWF – World Wildlife Fund, the extraction and spilling of fossil fuel can heavily impact the animal, human and marine lives.

- Nuclear energy: While nuclear energy does not produce greenhouse gas emissions during operation, the extraction and mining of uranium can have negative impacts on the environment, including water pollution and habitat destruction. On the other hand, nuclear power plants can produce produces hazardous waste that must be stored safely for thousands of years. Additionally, accidents at nuclear plants can tremendously affect the peoples living and working near to the nuclear plant. In the past, we have seen the horrible accidents of nuclear power plants in Chernobyl and Fukushima Daiichi, which resulted tremendous suffering of the local people.

What is the impact of non-renewable energy on industry and transportation?
Non-renewable energy sources have been the primary source of energy for the industry and transportation sectors for decades. According to the International Energy Agency data, 80% of the world’s energy used in transportation and industries comes from non-renewable sources.
Without non-renewable energy, it would be challenging to maintain the current level of industrialization and transportation. The use of non-renewable energy sources in these sectors provides:
- Reliable and continuous energy supply: Non-renewable energy sources provide a steady and dependable energy supply for industry and transportation, ensuring that production and transportation remain operational.
- High energy density: Non-renewable energy sources have a high energy density, meaning that they can produce large amounts of energy in a small space, making them ideal for powering vehicles and heavy machinery.
- Accessibility: Non-renewable energy sources are widely available, making them easily accessible for powering industry and transportation.
How does non-renewable energy impact modern-day technology?
Non-renewable energy sources have played a significant role in advancing modern technology. Non-renewable energy sources provide:
- High energy density: Non-renewable energy sources have a high energy density, making them ideal for powering modern technology, including data centres, servers, and telecommunication networks.
- Efficient energy production: Non-renewable energy sources have efficient energy production systems, making them ideal for powering modern technology that requires a lot of energy.
What is the impact of non-renewable energy on the environment and climate change?
The extraction, production, and use of non-renewable energy sources have significant negative impacts on the environment and contribute to climate change. The impact of non-renewable energy on the environment includes:
- Air pollution: Non-renewable energy sources produce large amounts of air pollutants and greenhouse gasses, including carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which contribute to respiratory diseases and acid rain.

- Water pollution: Non-renewable energy sources can contaminate water sources through oil spills and other industrial processes, affecting aquatic life and human health.
- Land degradation: The extraction and production of non-renewable energy sources can result in the degradation of land, including deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat destruction.

- Climate change: Non-renewable energy sources are a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, which are the main cause of global warming and climate change. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) data of 2022 , if we don’t reduce greenhouse emissions immediately, there is a chance of global warming of 1.5-2 degrees or beyond in the next decade. Another major problem is, global warming due to greenhouse emissions can lead to the melting of polar ice caps and the rise of ocean levels. As a result, many countries located near sea level can go underwater in future.

How does non-renewable energy impact public health and safety?
Non-renewable energy sources can have significant impacts on public health and safety, particularly for workers and communities living near energy production facilities. The impact of non-renewable energy on public health and safety includes:
- Occupational hazards: Workers in the energy production sector can be exposed to hazardous materials, including chemicals and radiation, which can cause serious health problems.
- Accidents and disasters: The extraction, production, and transport of non-renewable energy sources can result in accidents and disasters, including oil spills, explosions, and fires, which can have severe impacts on human health and the environment.
- Community health: Communities living near energy production facilities can experience air and water pollution, leading to respiratory diseases, cancer, and other health problems.
What is the impact of non-renewable energy on economics and geopolitics?
Non-renewable energy has played a significant role in shaping the global economy and geopolitical landscape. Countries that have an abundance of non-renewable energy resources, such as oil (middle eastern countries) and gas, have historically been major players in the global economy. They have been able to leverage their resources to create significant wealth, build infrastructure, and develop their economies. However, this dependence on non-renewable energy has also made them vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil and gas prices and geopolitical tensions.
Non-renewable energy has also been a source of geopolitical conflict. Countries that rely on non-renewable energy resources often use them as a tool to exert influence over other countries. On the other hand, geopolitical crises or wars can influence the supply chain of non-renewable energy sources; as a result, we can suffer a big fluctuation in price. Recently we have seen that, due to Russia and Ukraine war, there is huge shortage of energy in Europe. Russia is major producer of oil and gas. Due to the Russia and Ukraine war the supply chain of oil and gas has been influenced heavily, as a result we are suffering worldwide inflation.
What is the social impact of non-renewable energy?
The use of non-renewable energy sources has a significant social impact. Here are some of the ways in which non-renewable energy can affect society:
- Job creation: The non-renewable energy industry, including oil and gas extraction and coal mining, creates many jobs, both directly and indirectly.
- Access to electricity: Non-renewable energy sources like coal and natural gas are used to generate electricity, which is essential for modern life.
- Economic growth: The availability of non-renewable energy resources can drive economic growth, particularly in developing countries.
What is the future of non-renewable energy?
The short answer is Unstable! As concerns about climate change and environmental degradation continue to grow, there is a growing push towards renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, hydroelectric power and geothermal energy. While non-renewable energy sources will likely continue to play a significant role in the global energy mix for many years to come, there is a growing recognition that we need to move towards a more sustainable and renewable energy future.
What are the alternatives to non-renewable energy sources?
There are several alternative sources of energy that are considered renewable, including:
- Solar energy: Generated by harnessing the power of the sun through solar panels.
- Wind energy: Generated by harnessing the power of the wind through wind turbines.
- Hydroelectric power: Generated by harnessing the power of moving water.
- Geothermal energy: Generated by harnessing the heat from the Earth’s core.
- Biomass: Generated by using organic matter such as wood chips, agricultural waste, or municipal waste.
Wrapping up!
Me as a person, who works in the area of research in solar cells, I wish to see a green, clean and sustainable future for mother earth. But, non-renewable energy has played a significant role in shaping the modern world, powering industries, transportation, and modern technology. However, the continued use of non-renewable energy can lead to disaster, since it has significant negative impacts on the environment, public health, and the economy. As we move forward, there is a growing recognition of the need to transition toward a more sustainable and renewable energy future.
Important links to the sources that helped me to write this article:
- Department of Energy : https://www.energy.gov/
- National Geographic: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/
- IPCC — Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: https://www.ipcc.ch/
- International Energy Agency: https://www.iea.org/
- World Nuclear Association: https://world-nuclear.org/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)