Last updated on March 2nd, 2025 at 03:45 pm
Wind energy is a source of renewable energy and it is becoming popular with time. This type of energy doesn’t produce greenhouse emissions unlike non-renewable energy sources and it provides a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. In the United States, wind energy is the largest source of renewable energy and it produces 10.2% of the country’s total electricity.
Let’s start with an interesting story of my personal experience related to wind energy and wind turbines. In 2014, I visited Eindhoven in the Netherlands for the first time. As I was leaving the city (don’t remember the exact location), I stumbled upon a sight that left me awestruck. Amidst the barren fields, stood towering giants dressed in white, moving in a synchronized rhythm – it was a wind farm! For the first time in my life, I was witnessing the marvel of wind energy.
Some may argue that these turbines mar the natural beauty of the landscape, but to me, they added an ethereal charm that was impossible to ignore. As I gazed at them, I couldn’t help but wonder about the sheer magnitude of energy being harnessed by these graceful giants.
It was then that I realized the true power and potential of wind energy, and I left the Netherlands with a newfound appreciation for this incredible renewable energy source.
In this article, we will explore the basics of wind energy and wind turbines, how it works to generate electricity, and their potential impact on the environment, wildlife, economy, and job creation. In addition to that, we will also discuss the recent advancement in the area of the wind energy sector.
What is wind energy?
Wind energy is the process of using the kinetic energy of the wind to generate electricity. This is typically done using wind turbines, which are tall towers with large blades that rotate when the wind blows past them. The rotation of the blades drives a generator that produces electricity, which can then be used to power homes, businesses, and other facilities.
What are the different types of wind energy?
- Land-Based Wind Energy: In this type of wind energy wind turbines are located on land, such as in fields or on hillsides. Land-based wind energy is a renewable and sustainable source of energy, and it has the potential to significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels.
- Distributed Wind Energy: This refers to wind turbines that are located near the point of use, such as on farms, businesses, or homes. Unlike large-scale wind farms, distributed wind energy systems generate electricity that is consumed locally, rather than being sent to a centralized power grid. This can help to reduce transmission losses and increase energy efficiency.
- Offshore Wind Energy: This refers to wind turbines that are located offshore, typically in the ocean. Offshore wind energy has several advantages over land-based wind energy, including stronger and more consistent winds, and less noise pollution. However, offshore wind energy systems are typically more expensive to install and maintain than land-based systems, and they may face additional regulatory hurdles. One of the biggest offshore wind farms in the world is the Hornsea Wind Farm in the UK. The wind farm has a capacity of 1.2 GW and consists of 174 wind turbines located 120 km off the Yorkshire coast. The project is expected to generate enough electricity to power over 1 million homes.
- Utility-Scale Wind Energy: Utility-scale wind energy refers to large-scale wind energy projects that are typically owned and operated by utilities or independent power producers. These wind farms can generate hundreds of megawatts of electricity and are usually located in areas with high wind resources, such as open plains or coastal regions.
- Hybrid Wind Energy Systems: Hybrid wind energy systems combine wind turbines with other renewable energy sources, such as wind-solar hybrid systems, to provide a more reliable and consistent source of power. These systems can be used in remote areas or off-grid locations where there is no access to traditional power grids.
What is the difference between offshore and onshore wind energy?
The main difference between offshore and onshore wind energy is the location of the wind turbines. Onshore wind turbines are located on land, typically in open fields or on hilltops, while offshore wind turbines are located in bodies of water, such as oceans or lakes.
Offshore wind turbines tend to be larger and more powerful than onshore turbines because they have access to stronger and more consistent wind resources. However, they are more expensive to build and maintain and require specialized equipment and installation methods. Onshore wind turbines, on the other hand, are generally less expensive and easier to install, but may not have access to the same quality and consistency of wind resources as offshore turbines.

Do you know? The China State Shipbuilding Corporation (CSSC) is constructing the world’s largest and most powerful offshore wind turbine, the H260-18MW, with a peak capacity of 18 megawatts and a rotor diameter of 260 meters (853 feet) featuring three blades. The previous record holder for the biggest wind turbine was the MingYang Smart Energy MySE 16.0-242, which uses 118-meter (387-foot) blades to sweep an area of 46,000 square meters (495,140 square feet).
How do wind turbines generate electricity?
Wind turbines work by harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind and converting it into electrical energy. Let’s know how these rotating giants generate electricity for us!
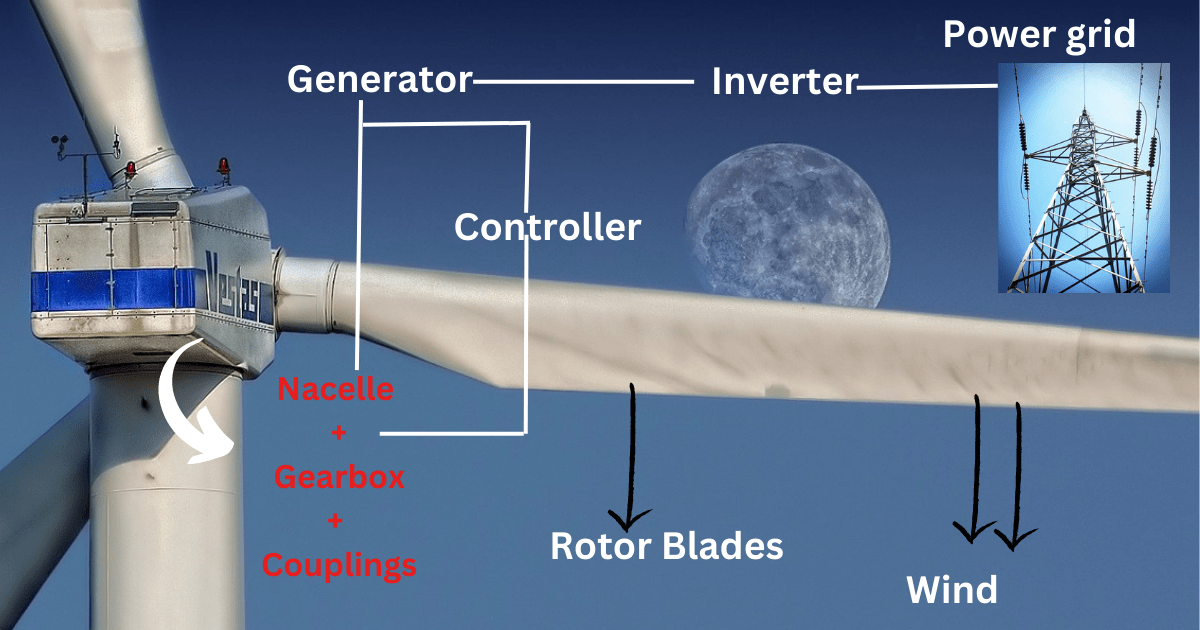
The process begins with the rotor blades, which are designed to capture the kinetic energy of the wind as it blows across the surface of the blade. As the wind pushes against the blades, they begin to rotate around the central hub of the wind turbine.
The rotational energy produced by the rotor blades is then transmitted to the gearbox, which is located inside the nacelle. The gearbox transmits the energy to the generator. The generator converts the rotational energy into electrical energy
Wind turbines also include a range of control systems that are designed to optimize the performance and efficiency of the wind turbine. These control systems monitor the speed and direction of the rotor blades and adjust them to optimize the amount of energy being produced. The control systems also include safety features, such as the braking system, which is designed to stop the rotor blades from rotating in the event of an emergency or when maintenance is required.
The electrical energy produced by the generator is typically in the form of alternating current (AC) electricity. However, an inverter is needed to connect this electricity to the power grid. The role of the inverter in a wind turbine is to convert the variable frequency and voltage of the AC electricity produced by the generator into a fixed frequency and voltage AC electricity that is synchronized with the grid. This is necessary to ensure that the electricity produced by the wind turbine can be efficiently and safely integrated into the electrical grid.
Do you know? The first wind turbine was invented in 1888 by Charles F. Brush in Cleveland, Ohio
What is the impact of wind energy on the United States?
Wind energy is a game-changer for the United States! According to the US Energy Information Administration data of 2022, wind power is the leading renewable source of electricity in the United States, supplying 10.2% of the country’s total electricity and still growing.
Following American Clean Power data, in 2021, the wind energy sector supported over 120,000 jobs across all 50 states and it contributed to a quarter of the electricity produced in eight states.
In addition to its economic benefits, wind energy is also an environmentally friendly choice, capable of preventing 340 million metric tons of CO2 emissions each year. It’s no wonder that the wind energy industry in the United States has received $135 billion in investments over the past decade, with $12 billion invested in new projects in 2021 alone.
The wind energy sector in the USA is predicted to see substantial growth in the coming years, with wind turbine technician being the second-fastest-growing job in the country, expected to increase by 44% over the next decade. Wind energy projects also provide significant financial benefits to state and local governments, generating an estimated $1.9 billion in annual tax and land-lease payments.
What are the 5 advantages and disadvantages of wind energy?
Advantages:
- Renewable and sustainable: Unlike non-renewable energy sources wind energy does not produce any emissions or pollutants. It is sustainable and can be used as long as the wind continues to blow.
- Cost-effective: Wind energy is one of the most cost-effective sources of energy available today. Once a wind turbine is installed, the cost of generating electricity is very low compared to other sources.
- Creates jobs: The wind energy industry is a growing industry that creates jobs for people. From manufacturing and installation to maintenance and operation, there are many jobs associated with wind energy.
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels: Wind energy helps to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels, which are non-renewable and contribute to climate change.
- Low land use: Wind turbines can be installed on land that is not suitable for agriculture or other uses, which means that they do not compete with other land uses.
Disadvantages:
- Dependence on the weather: Wind energy is dependent on the weather, and if there is not enough wind, the wind turbines cannot generate electricity. This can be a problem in areas with low wind speeds.
- Visual impact: Wind turbines can be large and visually intrusive, which can be a concern for some people, especially in areas of natural beauty.
- Noise pollution: Wind turbines can produce noise pollution, which can be a concern for people living near wind farms.
- Wildlife impact: Wind turbines can have an impact on wildlife, particularly birds and bats, which can be killed or injured by the spinning blades.
- Maintenance and operation: Wind turbines require regular maintenance and operation to ensure that they continue to function properly. This can be expensive and time-consuming.
Fun fact: Wind turbines have come a long way in terms of design and technology, with modern turbines standing as tall as 80-story buildings and weighing up to 400 tons.
Solar vs Wind Energy comparison
Solar and wind energy are the two most popular sources of renewable energy. Each one of them has advantages and disadvantages. Let’s compare them:
| Comparison Criteria | Solar energy | Wind energy |
| Energy source | Kinetic energy of wind | Radiant energy from the sun |
| Availability | Depends on sunlight intensity and duration | Depends on wind speed and consistency |
| Efficiency | Solar panels can convert up to 22% (more or less) of solar energy into electricity | Can convert up to 59% of wind energy into electricity |
| System lifetime | 20-30 years | 20-25 years |
| Cost | Installation cost is decreasing, but can still be expensive, and operational costs can be high | Initial installation costs can be high, but long-term operational costs are low |
| Energy density | Lower energy density, requiring large solar panel arrays | Higher energy density, with smaller turbines able to generate more power |
| Power output | Lower power output than wind energy, but can be increased with larger installations | High power output, especially in areas with consistent wind. However, it depends on wind speed and turbine size |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, no moving parts | Regular maintenance required for turbines |
| Land Use | Large area required for utility-scale installations | Smaller land area is required for the same power output compared to solar |
| Environmental impact | Minimal impact, but some environmental concerns with the manufacturing and disposal of solar panels | Can have a negative impact on bird and bat populations, noise pollution, and visual impact |
| Geographical location | Best in areas with high solar irradiance, such as deserts or sunny regions | Best in areas with consistent wind, such as coastal or high-altitude areas |
| Applications | Rooftop and ground-mounted solar installations, as well as large-scale solar farms. Good for small-scale and residential use | Large-scale energy production, including utility-scale and community wind projects |
| Grid integration | Solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, which is converted into alternating current (AC) electricity through an inverter. The AC electricity can then be connected to the electrical grid through a transformer to match the voltage of the transmission grid. | Generally wind turbines generate AC electricity and it can be integrated into the power grid directly. |
| Energy storage | Requires expensive batteries or other storage methods | Can integrate with battery storage or other energy storage methods |
| Future potential | Solar panel technology is advancing, with the potential for increased efficiency and lower costs | Wind turbines are becoming more efficient and less expensive, and offshore wind has significant growth potential |
Impacts of wind energy on the environment, wildlife, economy and job creation
Impact of wind energy on the Environment and Wildlife
Wind energy is a clean and renewable source of energy that has minimal environmental impact compared to non-renewable sources of energy. Wind turbines do not produce harmful emissions or pollutants, making them an environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels.
However, like any form of energy production, it has some potentially negative impacts on the environment and wildlife that need to be addressed.
According to the United States Geological Survey, wind turbines can pose a risk to birds and other wildlife if they are not properly located and maintained. Birds can collide with the turbines, and the spinning blades can also pose a risk to bats and other flying animals.
To minimize these risks, wind turbines are often located away from bird migration routes. However, modern wind turbines are designed to minimize this risk by using slow-moving blades, sensors that can detect approaching wildlife, and other measures to minimize bird and bat collisions.
Despite these risks, studies have shown that wind turbines are responsible for a small fraction of bird deaths compared to other human-related causes such as buildings, cars, and power lines.
Despite these impacts, wind energy is still considered to be one of the most environmentally friendly sources of energy available. Proper planning and location of wind turbines can help to mitigate negative impacts and allow for increased use of wind energy while minimizing harm to the environment.

Impact of wind energy on economy and job creation
Wind energy has become a significant contributor to the global energy mix, with its usage growing rapidly over the past few decades. The impact of wind energy on the economy has been positive in various ways.
Wind energy has created a large number of job opportunities in various sectors. The installation, operation, and maintenance of wind turbines require skilled and unskilled labor, which has created jobs in the manufacturing, construction, engineering, and maintenance industries. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the global wind energy sector employed over 1.2 million people in 2018.
The growth of wind energy has resulted in an increase in economic activity, particularly in rural areas. Wind farms generate income for landowners, provide tax revenue for local governments, and stimulate economic activity in the form of increased tourism, service industries, and construction.
According to the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC) report of 2021, wind energy alone can create 3.3 million jobs until 2026. China, Brazil, the US, and India are the countries with the most wind energy jobs. According to the market intelligence of GWEC, the wind industries all around the world plans to 470 GW of new onshore and offshore wind capacity between 2021-2025.
These types of massive-scale wind turbines installation around the world will create 3.3 million new jobs in the countries like China, the US, India, Germany, UK, Brazil, France, Sweden, Spain, South Africa, and Taiwan, and these jobs will be created during the construction, operation, and maintenance phases of projects.
In addition to that, the cost of wind energy has been decreasing over the years, making it increasingly competitive with fossil fuel-generated electricity. As the cost of wind energy continues to decline, it is expected to provide significant economic benefits.
What are the top 10 countries that produce wind energy the most?
According to the data of 2022, here is the list of 10 countries which generates the wind energy the most:
- China: China is the world’s leading producer of wind energy, with an installed capacity of over 366 GW. The country has been rapidly expanding its wind power capacity in recent years, driven by government policies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
- United States: The United States is the second-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 141 GW. Wind power accounts for about 10.2% of the country’s total electricity generation, and it is expected to continue to grow as more states adopt renewable energy goals.
- Germany: Germany is the third-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 66 GW. The country has a long history of investing in renewable energy and has set a goal to generate 65% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
- India: India is the fourth-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 41 GW. In 2015, India had set a target of achieving 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022, including 60 GW from wind power.
- Spain: Spain is the fifth-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 29 GW. The country has been a leader in renewable energy for many years and has set a goal to achieve 100% renewable electricity by 2050.
- United Kingdom: The United Kingdom is the sixth-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 28 GW. The country has set a target of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 and has been rapidly expanding its offshore wind power capacity.
- Brazil: Brazil is the seventh-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 24 GW. The country has been rapidly expanding its wind power capacity in recent years and has set a target of generating 28% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
- France: France is the eighth-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 21 GW. The country has set a target of generating 40% of its electricity from renewable sources by 2030.
- Canada: Canada is the ninth-largest producer of wind energy in the world, with an installed capacity of over 15.2 GW. The country has set a goal of achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 and has been expanding its wind power capacity to help achieve this goal.
- Sweden: Sweden is the tenth-largest producer of wind energy in the world with an installed capacity of over 14.5 GW. The country is a major player in renewable energy development in Europe, with a goal of becoming carbon-neutral by 2045.
What is a windmill?
A windmill is a machine that converts the kinetic energy of the wind into rotational energy for grinding grains (such as wheat, corn, or rice), pumping water, or generating electricity. Windmills have been used for hundreds of years and are still used in some parts of the world today.
The basic structure of a windmill is typically the same as the wind turbines, consisting of blades or sails mounted on a rotating shaft or rotor.
There are some historic windmills around the world such as the Kinderdijk windmill in the Netherlands and the Moulin de la Galette windmill located in Paris, France. Kinderdijk has been UNESCO World Heritage since 1997 and this group of 19 windmills was built in the 18th century to drain the surrounding area and prevent flooding.
The Moulin de la Galette was built in the 17th century and was used for grinding flour and pressing the local grapes and it was used until the 19th century. Moulin de la Galette is actually a combination of two different windmills: Moulin Radet and Moulin de Blute-Fin. It is now a popular tourist attraction and is known for its iconic red sails.

Recent Advancements and Development in Wind Energy
There have been several recent advancements and developments in wind energy technology. One promising development is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to optimize wind turbine performance.
The data collected from wind turbines can be analyzed using AI and ML algorithms to identify patterns and optimize turbine performance. For example, the algorithms can detect changes in wind speed and direction and adjust the turbine’s angle and rotor speed to maximize energy output. The algorithms can also identify maintenance needs and predict potential failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Another recent development is the use of floating wind turbines, which can be deployed in deeper waters where wind speeds are higher. Floating wind turbines have the potential to unlock new areas for wind energy development, such as off the coasts of Hawaii and California.
The main focus of wind turbine innovation is to increase productivity, especially in low-wind areas. Onshore wind turbines have limitations on height, which restricts innovation possibilities, while offshore turbines can be made larger to reduce power generation costs. Floating offshore wind turbines are being developed as a cost-effective and safe solution to unlock the potential of ocean areas with a water depth too deep for fixed turbines.
One example of a floating wind turbine is the Hywind Scotland wind farm, located off the coast of Aberdeenshire in Scotland. The wind farm consists of five floating turbines, each with a capacity of 6 MW, making it the world’s first floating wind farm.
The Future of wind energy
Wind energy is expected to have a bright future due to its numerous advantages such as being clean, renewable, and cost-effective. The use of larger wind turbines and advancements in technology, including energy storage and smart grids, will help to improve wind energy efficiency and reliability. Additionally, the continued growth of the wind energy industry is expected to create jobs and contribute to economic development.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA) data, wind energy is becoming increasingly popular as a source of renewable energy. In 2021, wind energy generation increased by 17% and almost 1,870 TWh (terawatt-hour) of electricity was generated, making wind the leading non-hydro renewable technology.
According to IEA data, offshore wind technology has seen the highest growth, delivering 22% of total wind energy capacity growth in 2021, which is three times the average of the previous five years. China was responsible for 80% of this offshore growth. To reach the goal of net-zero emissions in 2030 by generating 8,000 TWh of wind electricity, both onshore and offshore farms require increased support.
Final Words!
In conclusion, wind energy has proven to be a game-changer in the field of renewable energy, with its remarkable growth rate and potential to revolutionize the energy industry. As we look forward to achieving 2030’s Net Zero Scenario’s annual wind electricity generation, will require a concerted effort to increase support for both onshore and offshore wind farms. As a result, wind energy is becoming an increasingly important part of the global energy mix.
It has the potential to provide a significant source of clean, renewable energy for many countries around the world. With the advancements in wind turbine technology, such as the use of artificial intelligence and the development of floating wind turbines, wind energy is poised to become even more efficient and cost-effective in the coming years. While some may have concerns about the visual impact of wind turbines, but for others, like myself, they can be a beautiful and awe-inspiring sight.
Sources
- Department of Energy: https://www.energy.gov/
- National Geographic: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/
- IPCC — Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: https://www.ipcc.ch/
- International Energy Agency: https://www.iea.org/
- US Energy Information Administration: https://www.eia.gov/
-
Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC): https://gwec.net/
-
International Renewable Energy Agency: https://www.irena.org/
- United States Geological Survey: https://www.usgs.gov/