Last updated on March 4th, 2025 at 02:56 pm
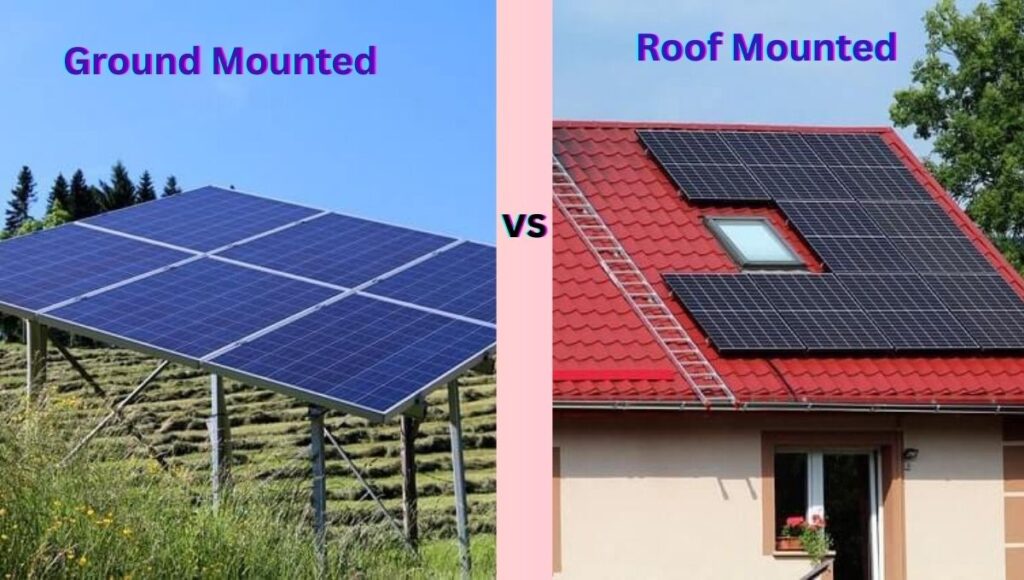
When it comes to choosing the right solar panel installation method, the debate between ground-mounted vs roof mounted solar panels often arises. Both ground-mounted and roof-mounted solar panels offer unique advantages and considerations. Factors such as available space, sun exposure, property characteristics, aesthetics, and cost play a crucial role in deciding between the two.
After reading this article, you will have a comprehensive overview of the differences between ground-mounted and roof-mounted solar panels, enabling you to make an informed decision based on your specific circumstances. You will gain insights about the advantages, considerations, and key factors to consider when choosing between these two installation methods.
What is a ground-mounted solar panel?
A ground-mounted solar system is an innovative and versatile approach to harnessing the power of the sun. Instead of being confined to rooftops, solar panels are strategically positioned on the ground or low structures, unlocking a range of benefits.
These solar systems utilize sturdy racks or frames to hold the solar panels at an optimal angle and orientation, maximizing their exposure to sunlight throughout the day. By capturing more sunlight, ground-mounted systems can achieve increased efficiency and generate higher amounts of clean, renewable energy compared to traditional rooftop installations.
What is a roof-mounted solar panel?
A roof-mounted solar system is a type of solar energy installation where solar panels are securely mounted on the roof of a building. These photovoltaic (PV) panels harness sunlight and convert it into usable electricity, offering numerous benefits for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
In this configuration, solar panels are strategically positioned on the existing roof structure using specialized mounting systems. These mounting structures ensure that the panels are securely fastened while optimizing their angle and orientation for maximum sunlight absorption.

Ground-mounted system: Pros and cons
Pros of a ground-mounted solar panel
-
Flexibility in Installation: Ground-mounted solar systems offer more flexibility in terms of placement and orientation compared to rooftop systems. They can be installed in any open space on your property that receives adequate sunlight, allowing you to optimize the system’s position for maximum energy production.
-
Increased Energy Production: Ground-mounted systems can be positioned to capture sunlight more efficiently throughout the day. They are not limited by roof angles or shading from surrounding structures, which can result in higher energy production compared to rooftop systems.
-
Easier Maintenance and Cleaning: Ground-mounted solar panels are easily accessible, making maintenance and cleaning tasks simpler and safer. There is no need to climb onto the roof for inspections or repairs, reducing the associated risks.
-
Scalability: They are generally easier to expand or upgrade compared to rooftop installations. If you have available land, you can easily add more panels to increase your solar capacity as your energy needs grow.
-
No Roof Limitations: Unlike rooftop systems, ground-mounted solar installations are not affected by the size, shape, or condition of your roof. This makes them suitable for buildings with complex or non-ideal roof structures. Additionally, ground-mounted systems can be installed at the optimal tilt and orientation for your location, maximizing energy production.
-
Aesthetics and Design: Ground-mounted solar arrays can be designed in various configurations and layouts, allowing for more aesthetic options. They can be integrated into the landscape or positioned to align with specific design preferences. This can be particularly advantageous for properties where rooftop installations may not be visually appealing or desired.
-
Reduced Roofing Costs: By opting for a ground-mounted system, you eliminate the need for potential roof modifications or the risk of damage during installation. This can save you money on roofing repairs or replacements that may be required for rooftop installations.
-
Safety and Fire Risk: Ground-mounted solar systems reduce the risk of fire spreading to your home or other structures in case of a panel malfunction or fire. Additionally, in the event of a fire, emergency responders have easier access to the solar array from the ground, enabling them to extinguish the fire more effectively.
Cons of a ground-mounted solar panel
-
Land Requirement: Ground-mounted systems require a significant amount of land space compared to rooftop installations. If you have limited available land, it may not be feasible to install a ground-mounted system that meets your energy needs.
-
Increased Installation Cost: They generally have higher installation costs compared to rooftop installations. The cost of preparing the site, including excavation, foundation construction, and wiring, can add to the overall expenses.
-
Potential Land Use Conflict: In some cases, utilizing land for solar installations may conflict with other potential uses. If you have limited open space or if the land is needed for other purposes such as agriculture or construction, a ground-mounted system may not be the most suitable option.
-
Visual Impact: Depending on your preferences and the location of the system, a ground-mounted solar array can have a more visible impact compared to rooftop installations. Some people may find the appearance of large solar panels on the ground less aesthetically pleasing or may be concerned about the impact on the surrounding landscape.
-
Accessibility Limitations: While ground-mounted systems offer easier access for maintenance and cleaning, they can also pose accessibility challenges in certain situations. If the installation is located far from the main property or if the terrain is difficult to navigate, it may be more challenging to reach the system for routine maintenance or repairs.
-
Vulnerability to Damage: Ground-mounted systems are generally more exposed to potential damage from animals, vandalism, or accidental impact compared to rooftop installations. Additional measures such as fencing or security systems may be required to protect the system from potential risks.
-
Potential for Obstruction: Ground-mounted solar arrays can be subject to potential obstructions such as nearby trees or future construction that may shade the panels and reduce energy production. Careful consideration of the site and its surroundings is essential to ensure long-term unobstructed sunlight exposure.
-
Permitting and Regulatory Requirements: Depending on your location, ground-mounted systems may have specific permitting and regulatory requirements that can involve additional time and costs. It is important to research and comply with local regulations before proceeding with the installation.
Key considerations before installing a ground-mounted solar panel
When it comes to installing a ground-mounted solar system, there are several important factors to consider. Ground mounts offer flexibility and ease of access, but proper planning and assessment are crucial for a successful installation. Let’s dive into the key aspects you should keep in mind.
1. Available Space
One of the first things to consider is the amount of available space on your property. Ground-mounted solar systems require a significant area to accommodate the panels and support structures. Assess your land to ensure it has enough unobstructed space that receives adequate sunlight throughout the day. Consider factors like existing structures, trees, and potential shading from nearby buildings.
2. Sunlight Exposure
Solar panels rely on sunlight to generate electricity, so it’s crucial to evaluate the sunlight exposure on your chosen ground mount location. Look for an area with maximum exposure to the sun throughout the year. Take into account any potential shading from surrounding objects, as even partial shading can significantly impact the performance of the solar system.
3. Land Slope and Terrain
The slope and terrain of your land can affect the installation process and overall system performance. Ideally, a flat or gently sloping area is preferred for easier installation and maintenance. If your land has a significant slope, additional leveling or grading may be necessary, which can increase the cost and complexity of the installation. Assessing the land’s stability and drainage is also important to ensure long-term durability.
4. Ground Preparation
Ground mounts require proper foundation and anchoring to ensure stability and longevity. Depending on the soil type and local conditions, the installation may require excavation, concrete footings, or other appropriate foundation systems. Consider the cost and complexity of the ground preparation work and consult with professionals to determine the best approach for your specific site.
5. System Size and Expansion
Ground-mounted systems offer scalability and can be easily expanded in the future if needed. Consider your current and future energy needs when determining the size of the system. Assess the available land to ensure there is ample space for potential system expansion without compromising the performance of existing panels. Planning for future growth can save you time and money in the long run.

Roof-mounted system: Pros and cons
Pros of a roof-mounted solar panel
-
Space Utilization: Roof-mounted solar systems make efficient use of available space on your roof, which is often unused or underutilized. By utilizing your roof for solar panels, you can generate clean energy without compromising additional land or property space.
-
Optimal Sun Exposure: Roofs often provide excellent sun exposure, especially if they face south (in the northern hemisphere) or north (in the southern hemisphere). Solar panels on the roof can capture sunlight throughout the day, maximizing energy production. The tilt of the roof can also be adjusted to optimize the angle for solar absorption.
-
Reduced Energy Loss: Roof-mounted systems minimize energy loss by reducing the distance between the solar panels and the energy consumption points within the house. With shorter wiring distances, there is less chance for energy loss during transmission, leading to higher overall system efficiency.
-
Integration with the Building: Roof-mounted solar systems seamlessly integrate with the architecture of the building, resulting in a visually cohesive appearance. The panels can be installed in a way that complements the roof design, making them less obtrusive or disruptive to the overall aesthetics of the property.
-
Protection for the Roof: Solar panels can provide an additional protective layer to your roof by shielding it from direct sunlight, rainfall, and other weather elements. They act as a barrier, reducing the wear and tear on your roof and potentially prolonging its lifespan.
-
Quicker Installation: Roof-mounted solar installations typically have shorter installation times compared to ground-mounted systems. The existing structure of the roof simplifies the installation process, reducing labor and material requirements.
-
Cost Savings: Installing solar panels on your roof can result in long-term cost savings on electricity bills. By generating your own clean energy, you can reduce or eliminate your reliance on grid-supplied electricity, saving money over the system’s lifetime. Additionally, many regions offer incentives, such as tax credits or net metering programs, that can further enhance the financial benefits of a roof-mounted solar system.
-
Safety and Security: Roof-mounted solar systems are less susceptible to theft or vandalism compared to ground-mounted systems. The elevated position of the panels makes them less accessible and helps deter potential intruders. Additionally, there is no risk of accidental damage from lawn equipment or vehicles, as the panels are out of reach on the roof.
Cons of a roof-mounted solar panel
-
Roof Condition and Lifespan: Before installing solar panels, it’s crucial to assess the condition of your roof. If your roof is old or in need of repairs, it may require maintenance or replacement before installing solar panels. This additional cost can impact the overall affordability of the solar system. Moreover, if you need to repair or replace your roof in the future, the solar panels will need to be temporarily removed and reinstalled, incurring additional expenses.
-
Shading and Sun Exposure: Shading can significantly impact the performance of a roof-mounted solar system. If your roof is partially shaded by trees, nearby buildings, or other objects, it can lead to reduced energy production. Even a small amount of shading on just one panel can affect the output of the entire system. It’s important to assess the shading patterns and potential obstructions before installing solar panels.
-
Roof Space Limitations: The available roof space determines the maximum capacity of your solar system. If your roof is small or has limited unobstructed space, you may not be able to install a solar system that meets your desired energy production goals. In such cases, a ground-mounted system or alternative solutions may be more suitable.
-
Roof Orientation and Tilt: The orientation and tilt of your roof can affect the efficiency of your solar panels. Ideally, a south-facing roof (in the northern hemisphere) or a north-facing roof (in the southern hemisphere) maximizes sun exposure. Roofs facing east or west may still be viable but can result in slightly reduced energy production. If your roof doesn’t have an optimal orientation or tilt, it can impact the overall system performance.
-
Roof Warranty and Penetration: Installing solar panels on your roof may impact the warranty provided by the roofing manufacturer. Roof penetrations during the installation process may void or limit the coverage. It’s important to review the terms of your roof warranty and consult with professionals to understand any potential implications before proceeding with a solar installation.
-
Maintenance and Accessibility: While roof-mounted systems are easily accessible during installation, they can pose challenges for maintenance and repairs. Routine inspections, cleaning, and repairs may require climbing onto the roof, which can be a safety concern or may require professional assistance. Accessibility issues can increase the cost and complexity of maintenance activities.
-
Aesthetics and Design: Some homeowners may have aesthetic concerns about the visual impact of solar panels on their roof. While efforts are made to integrate solar panels into the roof design, they can still alter the appearance of the property. If maintaining the original aesthetics of your roof is a priority, a roof-mounted solar system may not align with your preferences.
-
Heat Buildup and Ventilation: Solar panels absorb sunlight and generate heat, which can affect the roof’s temperature and ventilation. In some cases, this heat buildup can reduce the efficiency of the solar system or impact the longevity of the roof material. Proper ventilation and insulation are crucial to mitigate these effects.
Key considerations before installing a roof-mounted solar panel
There are several mounting ideas for solar panel installation. When considering a roof-mounted solar system, there are several important factors to keep in mind. Installing solar panels on your roof can be a great option for many homeowners, but it’s essential to consider these aspects to ensure a successful and efficient installation.
1. Roof Condition
Start by evaluating the condition of your roof. Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years, so it’s crucial to have a roof that can support the panels for their entire lifespan. If your roof is old or in need of repairs, it’s generally recommended to address those issues before installing solar panels. A structurally sound roof will provide a solid foundation for your solar system.
If your roof is nearing the end of its lifespan, you should consider whether it makes sense to install solar panels before replacing the roof. Solar panels are typically designed to last longer than most roofs, so installing them on an older roof may require removing and reinstalling them when the roof needs replacement. In such cases, it might be more cost-effective to replace the roof first and then proceed with the solar installation.
2. Roof Orientation and Tilt
The orientation and tilt of your roof play a vital role in maximizing the energy production of your solar panels. Ideally, your roof should face south in the northern hemisphere or north in the southern hemisphere to receive the most sunlight throughout the day. However, east and west-facing roofs can also be viable options, albeit with slightly reduced efficiency. Additionally, the pitch or tilt of your roof should be considered to ensure optimal solar exposure.
3. Shading
Shade can significantly impact the performance of your solar panels. Even partial shading on just one panel can lead to decreased energy production for the entire system. Before installing solar panels, evaluate the shade patterns on your roof throughout the day and year. Identify any potential sources of shading, such as trees, nearby buildings, or chimneys. It’s best to minimize shading to maximize the energy output of your system.
4. Roof Material
Different roof materials require different installation techniques. The most common roof types, such as asphalt shingles, metal, or concrete tiles, can typically accommodate solar panels. However, if you have a unique or fragile roof material, such as slate or cedar shakes, additional care and expertise may be required during the installation process. Ensure that the solar installer has experience working with your specific roof type.
5. Roof Load-Bearing Capacity
Solar panels add weight to your roof, so it’s important to assess its load-bearing capacity. Your roof should be able to support the additional weight of the solar panels, racking system, and any potential snow loads if you live in a snowy region. Consulting with a structural engineer or a qualified solar installer can help determine if your roof can handle the additional load.
Should you choose a ground or roof mounted solar panel?
When deciding between ground-mounted and roof-mounted solar panels, there are several factors to consider. Let’s explore these factors to help you make an informed choice that suits your needs and preferences.
Firstly, assess the available space on your property. If you have ample open land, a ground-mounted system might be a great option. It allows you to utilize that space efficiently for solar energy production. On the other hand, if your property has limited ground space but a sizable roof, roof-mounted panels can make efficient use of existing real estate.
Next, consider the sunlight exposure on your property. If you have unobstructed, sun-drenched land with optimal orientation and tilt, a ground-mounted system can capture maximum sunlight throughout the day. However, if your roof has good sun exposure, especially facing south (in the northern hemisphere) or north (in the southern hemisphere), roof-mounted panels can effectively harness the sun’s energy.
The condition of your roof is another important factor. If your roof is old, requires repairs, or is nearing the end of its lifespan, it may be more practical to address those issues before installing solar panels. Ground-mounted systems are independent of the roof condition, while roof-mounted systems may require additional expenses if roof repairs or replacements are needed.
Aesthetic preferences also come into play. Roof-mounted panels seamlessly integrate with your home’s architecture, creating a cohesive and visually appealing look. They blend with the existing design, making them an attractive option for those who value aesthetics. Ground-mounted systems offer more design flexibility, but keep in mind that they can have a more visible impact on the overall landscape.
Cost and installation complexity should be considered as well. Ground-mounted systems often require additional materials, excavation, and wiring, making them slightly more expensive to install. In contrast, roof-mounted systems tend to be more cost-effective as they utilize existing structures. However, if your roof requires repairs or replacements, it could add to the overall cost. Obtain quotes from reputable installers to compare costs based on your specific circumstances.
Finally, think about future expansion and flexibility. If you anticipate increasing your solar capacity in the future, ground-mounted systems offer greater scalability. They allow for easier system expansion without the constraints of roof space. On the other hand, if you don’t anticipate needing additional solar capacity, a roof-mounted system might suffice.
Closing thoughts!
In conclusion, the choice between ground-mounted and roof-mounted solar panels depends on your unique circumstances and priorities. Consider factors such as available space, sunlight exposure, roof condition, aesthetics, and cost. Ground-mounted systems offer flexibility, scalability, and design freedom, making them ideal for properties with ample open land.
Roof-mounted systems make efficient use of existing roof space, seamlessly integrating with the home’s architecture and often being more cost-effective. Assessing these factors and understanding your specific needs will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your energy goals and property characteristics. Remember, both options contribute to clean, renewable energy, so choose the one that suits you best.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)